What is hydropower
Hydropower is rain power, Rain falls high - rain flows into streams and rivers, dams it on its way to the sea and generates electricity through turbines so the number of sites is The places where you can generate electricity are limited! Rain must fall over a large area of high altitude in sufficient quantity to provide flow, and "fall" to be worth using
Example of hydropower
A hydroelectric power station converts the potential energy of a stream of water to electricity. The water source is usually a river. Ultimately, energy comes from the sun evaporating water from lakes and oceans and falling as rain to high altitudes. Pumped hydro is a variant that uses surplus power from wind, solar, or nuclear power to pump water uphill to a dam. This is a form of energy storage, also called pumped storage. It replaces batteries and other forms of energy storage
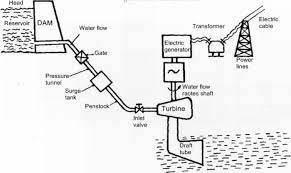
Hydropower energy system
Hydropower is the fifth oldest power source, after human power, fireplace, animal strength, and wind power, used by people. it's been used for lots of years.
In its number one modern-day application in strength era, hydropower in conventional configurations offer numerous crucial characteristics:
Like wind, sun, and electricity from biomass, hydro is renewable, deriving its strength from the atmospheric water cycle, that's pushed via the sun.
in contrast to biomass and fossil fueled power, there's no on-going manufacturing of CO2 and different emissions from the production and combustion of fuels.
in contrast to wind and sun energy, hydropower is dispatchable. that is, it can be made to be had as required via call for, and beyond that:
unlike electricity produced via combustion or nuclear, an hydropower set up may be configured with pumped storage. Pumped storage hydropower is a device (grid) balancing, resource maximizing characteristic. all through high gadget demand (normally throughout the day) the hydro-mills are operated at maximum output. Then in the course of low call for (commonly at night) water from the tail race is pumped back up to the impoundment. This makes positive that there's masses of water to be had throughout high call for whilst it is most precious by pumping it the use of power from the machine when it's miles priced lowest.
Benefits of hydropower
Renewable with zero carbon emissions (except construction), similarly low toxic emissions, reliability and significantly less environmental impact than fossil fuels. plus lower operating costs. and enhanced by enabling leisure activities